ii vom analiza toate link-urile si informatiile utile in vindecarea cancerului.
Primul link se refera la 5 medici morti si 5 medici - practicieni de metode alternative disparuti inaintea votarii la 30 iunie 2015 a legii privind obligativitatea vaccinarii.
Al doilea link, doctorul Jeff Bradstreet (61 de ani) gasit mort pe 19 iunie 2015, impuscat în piept.
Al treilea link, este mandatul judecătoresc care justica ca substanţa, care se numeşte Gc-MAF – Factor de Activare Macrofagică derivat din proteina Gc, reprezintă un produs greşit prezentat din punct de vedere al legii federale americane.
Dar, proteina Gc este un component care se produce de obicei în organism şi combinată cu vitamina D3, devine un factor major de activare a imunităţii, respectiv a celulelor macrofage, care „înghit” literalmente tot ceea ce atacă organismul: viruşi, bacterii, celule canceroase.
Al patrulea link trimite la: www.naturalnews.com:
"REVEALED: Cancer industry profits 'locked in' by nagalase molecule injected into humans via vaccines... spurs tumor growth... explains aggressive vaccine push" din 27 iulie 2015, autor Julie Wilson.
"Cei cinci doctori naturopaţi decedaţi în zonă recent erau cumva interconectaţi” prin interesul faţă de cercetările realizate de dr. Bradstreet şi de un al şaselea medic, dr. Nicholas Gonzalez, care trata cu succes cancerul la New York printr-o terapie alternativă cu enzime – decedat şi el în data de 23 iulie, aparent de infarct."
"Dr. Bradstreet şi alţi câţiva colegi descoperisera că activarea GcMAF în sistemul imunitar era compromisă de enzima cu numele Nagalază (eng. nagalase), produsă de obicei în mici cantităţi în intestin şi care serveşte la descompunerea unui anumit tip de glicoproteine din alimente. Când această enzimă este secretată în exces de celulele canceroase şi de cele infectate cu viruşi, ea împiedică combinarea proteinei Gc cu vitamina D3, ceea ce stopează producerea de GcMAF, care are loc doar cu ajutorul respectivei vitamine. Rezultatul este că celulele macrofage nu se mai activează, deci nu apare răspunsul imunitar adecvat la boală."
Surpriza surprizelor
Dr. Tim Smith, în cartea sa, The GcMAF Book, explică precizia uluitoare, in Capitolul 10, cu care nagalaza atacă proteina Gc, iar atunci când macrofagele nu sunt activate, nici ceilalţi „soldaţi” ai sistemului imunitar nu devin activi. O singură moleculă de nagalază poate distruge nenumărate proteine precursoare ale GcMAF.
Deci, aceasta carte se gaseste la link-ul: The GcMAF Book.
Acolo, in Capitolul 10 este reluata descoperirea din 2009 a biochimistului şi microbiologului american de origine japoneză Nobutu Yamamoto şi a colaboratorilor sai publicata în Journal of Medical Virology în care se afirmă in introducere despre cercetari mai vechi:
„Administrarea săptămânală de 100 ng GcMAF pacienţilor (n=32) cu adenocarcinom metastatic (cancer metastatic de sân şi de prostată) şi pacienţilor cu cancer colorectal metastatic distruge tumorile în 16–25 săptămâni, respectiv în 32–50 săptămâni. Cu aceeaşi procedură terapeutică, într-un studiu preliminar pe pacienţi infectaţi cu HIV, atât virionii liberi, cât şi celulele infectate cu HIV au fost distruse în 10–18 săptămâni”, adica:
"Weekly administrations of 100 ng GcMAF to metastatic adenocarcinoma (breast and prostatecancer) patients (n=32) and metastatic colorectal cancer patients eradicate tumors in 16-25 weeks and 32–50 weeks, respectively [Yamamoto and Ueda, 2004a; Yamamoto et al., 2005, 2008a,b,c]. With the same therapeutic procedure (i.e., administration of 100 ng GcMAF/week) in a preliminary study of HIV-infected patients, both cell-free virions and HIV-infected cells were eradicated in 10–18 weeks [Yamamoto and Ueda, 2004b; Yamamoto et al., 2007]."
Adica, chiar dacă nagalaza împiedică formarea de GcMAF în corp, ea nu poate împiedica acţiunea imunostimulatoare a acestui compus (GcMAF=Gc+ vitamina D3), dacă el este injectat direct pacientului.
Dacă la analize apare un nivel prea mare de nagalază în organism, atunci acest nivel indica prezenţa cancerului in organism într-un stadiu foarte incipient.
Oncologii nu ar trebui sa mai apeleze la mijloace imagistice scumpe pentru a stabili focarul cancerului, daca detecteaza nivel mare de nagalaza si simpla administrare de GcMAF ar remedia problema înainte de formarea vizibilă a tumorii.
Deci, pierd din start doua profituri: metodele scumpe devin inutile, iar medicamentele, chirurgia si radioterapia scumpe devin zero absolut.
Problema este că, de curând, studiile făcute de dr. N. Yamamoto şi colaboratorii săi au fost retractate din revistele de specialitate în care fuseseră publicate. Aceasta înseamnă discreditarea respectivelor cercetări din diverse motive.
Totusi, articolul "Immunotherapy of HIV-Infected Patients With Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage Activating Factor (GcMAF)" din Journal of Medical Virology 81:16–26 (2009) scris de Nobuto Yamamoto, Naofumi Ushijima, Yoshihiko Koga se regaseste la Journal of Medical Virology, dar se ocupa de terapia pacientilor cu HIV.
Un tratament ieftin şi eficient pentru cancer şi boli autoimune
Prin screeninguri periodice ale nivelului de nagalază s-ar putea preveni în mod relativ ieftin cancerul, o boală letală şi extrem de costisitoare, şi s-ar putea trata boli autoimune în prezent incurabile precum SIDA sau lupusul eritematos. Boli ca Parkinson, Alzheimer, artrita reumatoidă ar putea fi adăugate la această listă.
Inseram mai jos informatii clarificatoare de pe https://gcmaf.biz/:
Despre GcMAF
Ce este GcMAF?GcMAF is a protein made by all healthy people.
De ce unii oameni nu mai au in organism GcMAF?
Cancers and Viruses send out an enzyme called Nagalase that neutralises the bodies ability to make GcMAF. (without GcMAF our immune system goes to sleep)
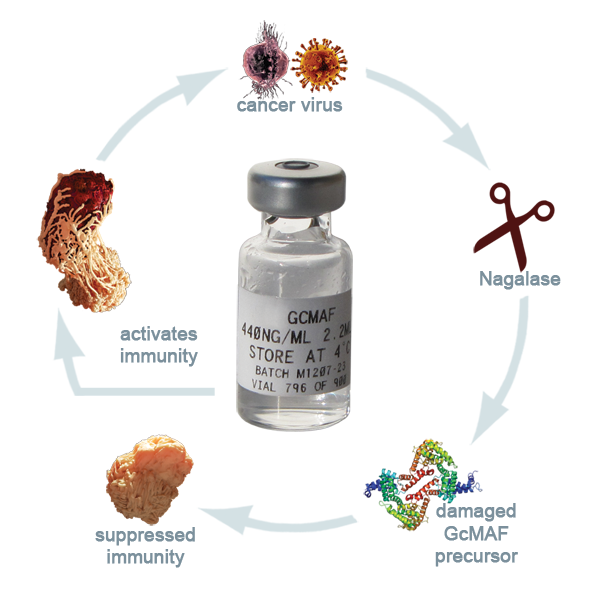
Ce putem face, daca organismul nu mai secreta suficienta GcMAF?
We make GcMAF outside the body and then administer it: orally, inhalation, injection or rectally)
Cum reactioneaza GcMAF in cazul cancerului? Link to Supporting Abstract
- GcMAF activates white blood cells in our tissue, called macrophages, to attack and digest cancers.
- GcMAF directly inhibits cancer cell proliferation and metastatic potential.
- GcMAF directly turns cancer cells back into healthy cells (reverts phenotype).
- GcMAF directly inhibits cancer cell-induced angiogenesis (stops blood supply to tumours).
- GcMAF induces apoptosis (suicide of cancer cells).
- OA-GcMAF suppresses HER2 oncogene expression in human breast cancer.
Cum lucreaza GcMAF in cazul altor boli?
"GcMAF modifies the expression of a number of genes in cells expressing the Vitamin D Receptor, which explains how it can be effective in such a variety of conditions ranging from cancer, to autism, ME, CFS, chronic kidney disease, neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases or Multiple Sclerosis as well as conditions associated with environmental pollutions."
Molecular Biologist, Professor Ruggiero, MD, PhD.
GcMAF ajuta intr-o serie de afectiuni
- Alzheimer's
- Autism
- Cancer
- Chronic Fatigue
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Hepatitis
- ME
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson's
- Psoriasis
La centrul său de wellness, dr. Bradstreet, naturopatul găsit împuşcat în piept, taxa cu 50 de dolari o injecţie cu GcMAF. Inspirat de studiile lui Yamamoto, el lucra la tratarea autismului prin această metodă. Împreună cu un grup de cercetători europeni, el a obţinut din practica clinică statistici (http://gcmaf.se/patient-resources/autism/) care arătau că, din peste 2.000 de copii autişti trataţi cu GcMAF de Dr Jeffrey Bradstreet, 15% erau complet recuperaţi, iar alţi 70% prezentau diverse nivele de îmbunătăţire a simptomelor.
Observând creşterea cu 23% a cazurilor de autism în numai doi ani, între 2006 şi 2008, dr. Bradstreet şi colaboratorii spuneau că proporţiile acestei afecţiuni au devenit epidemice. Autismul apare în primii trei ani de viaţă, iar copiii autişti prezintă niveluri ridicate ale infamei enzime denumite nagalază, deşi această particulă nu se găseşte şi în organismul nou-născuţilor. Aceasta l-a îndemnat pe dr. Bradstreet să creadă că ea este introdusă în organism prin procedurile de imunizare, adică prin vaccinuri, care de obicei conţin tulpini virale. Editorul website-ului NaturalNews.com crede că şi ceilalţi medici dispăruţi i-ar fi împărtăşit opinia.
David Noakes, fondatorul şi directorul executiv al Immuno Biotech Ltd (filiala ei operaţională din Guernsey - un ţinut insular din Canalul Mânecii, care depinde de Coroana Britanică, dar nu face parte din UE, a fost controlata de Agenţia Britanică de Reglementare pentru Medicamente şi Produse de Sănătate-MHRA), a declarat despre GcMAF pe care il produce că este absolut sigur şi eficient, deoarece compania face 9 teste de sterilitate pe toate produsele sale, folosind chiar laboratoarele guvernamentale în acest scop. El a amintit că şi în Olanda au avut necazuri similare, dar, după testare, autorităţile au confirmat sterilitatea perfectă a produselor lor, care au fost deja folosite de peste 9.000 de clienţi. Câteva mărturii ale acestora se găsesc aici:
"Human GcMAF, otherwise known as Vitamin D binding protein macrophage activating factor, holds great promise in the treatment of various illnesses including cancer, autism, chronic fatigue and possibly Parkinson's. Since 1990, 59 research papers have been published on GcMAF, 20 of these pertaining to the treatment of cancer. 46 of these papers can be accessed through the GcMAF web site."
Pentru mai multe informatii vizitati: First Immune GcMAF sau luati legatura cuDavid Noakes la:
First Immune GcMAF
Clos de Balade 21
1140 Evere
Brussels, Belgium
Noakes a spus despre GcMAF:
„Este o proteină umană fabricată în mod natural în organismul oamenilor sănătoşi. Are efect doar în 50 de boli şi la circa 60% din populaţie, un rezultat mult mai bun decât în cazul medicamentelor farmaceutice, despre care nu trebuie să uităm că sunt pe locul patru în topul cauzelor de mortalitate” (după cum o recunoaşte chiar FDA, Administraţia Americană pentru Alimente şi Medicamente pe website-ul său).
"Deci, GcMAF nu are efecte secundare, iar Agenţia Britanică de Reglementare pentru Medicamente şi Produse de Sănătate (MHRA) blochează accesul publicului la ştiinţa modernă şi protejează vechile monopoluri de miliarde de dolari ale companiilor farmaceutice, care îi finanţează. Sute şi mii de vieţi ar fi salvate dacă ei nu ar exista. Nici măcar nu le permit oamenilor să primească câteva miliardimi de gram de GcMAF, care este de fapt propria noastră proteină, fabricată chiar de corpul nostru. Practic, ei vor să pună licenţă nu pe un medicament, ci pe o parte a corpului uman”.
Ei nu pot abtine profit din GcMAF, pentru ca natura l-a inventat si blocheaza prin sistemul de licenţe accesul la remediu şi îngrijiri medicale. Ei vor sa faca accesul mult mai greu şi mai scump, din moment ce patentele puse pe substanţele artificiale şi metode de tratament permit crearea de monopoluri, care menţin preţurile mari.
Vizionati mai multe la:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1WZrnCcH24#t=13
Published on Oct 21, 2012
GcMAF eradicates cancer; cells seen via microscopes and time lapse photography.
This is a world wide first, and a scientific research paper named "Multifaceted immunotherapeutic effects of GcMAF on human breast cancer cells" peer reviewed, and published by us in the January 2013 Immunology Conference in San Diego.
Human MCF7 breast cancer cells are shown both in a corrugated layer on the surface below, and as irregular "fingers" above.
Macrophages are small round circles added at the bottom left. They do nothing until the First Immune GcMAF is added.
Time lapse photography over 60 hours shows the cancer monolayer below first changing from corrugated to smooth from the bottom left as the cancer is destroyed; then the cancer "fingers" are also eaten and destroyed by the macrophages.
This is part of the assays performed on batches of our GcMAF, and are carried out in First Immune (gcmaf.eu's) laboratories as part of our everyday production.
We supply 5,000 patients, 300 doctors in 30 nations.
This confirms the research paper "Effects of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor on human breast cancer cells," published in the journal "Anticancer Research", 2012 Jan; 32(1), 45-52, in which they also kindly used our First Immune GcMAF for their experiments.
There is a time lapse video of the 8th assay we do in our laboratory - our GcMAF activates macrophages that eat cancers cells. We are probably the only people in the world with this technology (https://gcmaf.se/ ).
Watch the video to see what happens to cancer cells when GcMAF is added without macrophages. This again is a world first, and again it has been done in our laboratory. Within just 4 weeks a research abstract paper on our results has already been accepted for publication at this year’s Immunology Conference in California.
Vedeti si filmul "GcMAF: THE AMAZING ANSWER FOR YOUR HEALTH".
Despre achizitii de GcMAF sunt disponibile urmatoarele informatii:
In prezent nu este posibila achizitia de GcMAF de pe site: https://gcmaf.se/gcmaf/This is a world wide first, and a scientific research paper named "Multifaceted immunotherapeutic effects of GcMAF on human breast cancer cells" peer reviewed, and published by us in the January 2013 Immunology Conference in San Diego.
Human MCF7 breast cancer cells are shown both in a corrugated layer on the surface below, and as irregular "fingers" above.
Macrophages are small round circles added at the bottom left. They do nothing until the First Immune GcMAF is added.
Time lapse photography over 60 hours shows the cancer monolayer below first changing from corrugated to smooth from the bottom left as the cancer is destroyed; then the cancer "fingers" are also eaten and destroyed by the macrophages.
This is part of the assays performed on batches of our GcMAF, and are carried out in First Immune (gcmaf.eu's) laboratories as part of our everyday production.
We supply 5,000 patients, 300 doctors in 30 nations.
This confirms the research paper "Effects of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor on human breast cancer cells," published in the journal "Anticancer Research", 2012 Jan; 32(1), 45-52, in which they also kindly used our First Immune GcMAF for their experiments.
There is a time lapse video of the 8th assay we do in our laboratory - our GcMAF activates macrophages that eat cancers cells. We are probably the only people in the world with this technology (https://gcmaf.se/ ).
Watch the video to see what happens to cancer cells when GcMAF is added without macrophages. This again is a world first, and again it has been done in our laboratory. Within just 4 weeks a research abstract paper on our results has already been accepted for publication at this year’s Immunology Conference in California.
Vedeti si filmul "GcMAF: THE AMAZING ANSWER FOR YOUR HEALTH".
Despre achizitii de GcMAF sunt disponibile urmatoarele informatii:
Acolo se sugereaza urmatoarele:
1. Compania japoneza Saisei Mirai ofera “Second Generation GcMAF.” Nu este GcMAF, este plasma obtinuta din sange dupa indepartarea hematiilor. Publicatiile lor nu arata rezultate incurajatoare.
2. Unii doctori prezentati pe acest site https://gcmaf.se au utilizat produsele Immuno Biotech si tin de companii profesioniste (added their tests to their already extensive testing, visited their laboratories or are in other ways familiar with them, and in our view they are easily the most professional company in this field).
Ei utilizeaza un proces de extractie in 24 de pasi pana la nivel molecular si testeaza lunar. Produsul poate fi administrat prin pulverizare, supozitoare sau oral, vezi www.immunobiotech.eu. Acestia vand un produs numit Goleic:
"Breast carcinoma phagocytosis activity assay. Macrophages are added to live MCF7 breast cancer cells; nothing happens. We add our Goleic; within 72 hours the macrophages are observed to phagocytise (eat and destroy) the cancer cells.
Third activity assay: we add our Goleic to MCF7 cancer cells without macrophages. On addition of Goleic a cell morphology change is observed In 72 hours where cancer cells adopt a normal cell morphology. (Experiment first performed by Professor Ruggiero’s team (with our Goleic) and published January 2012)
We have carried out about 100 assays on our Goleic."
3. O companie israeliana Efranat face teste cu GcMAF. Ofera o doza de GcMAF cu $1,000, dar multi care au utilizat aceasta spun ca nu cred ca este eficient. Probabil este inactiv.
Immune Support Protocol
The Swiss ProtocolThe Swiss Protocol is the intensive GcMAF protocol for treating Cancer.
Click to download the PDF instructions
Vitamin D3
GcMAF needs at least 10,000IU of vitamin D daily to work.
Oleic Acid
GcMAF needs Oleic acid to work. Take 5mls of Olive Oil daily.
Note: OA-GcMAF has Oleic acid bound to GcMAF, so no need to supplement with Olive Oil.
Bravo Super Shake
Patients following the Swiss Protocol receive a daily Bravo Super Shake that is designed to be an Immune Booster for advanced cancer support.
Click to download the PDF instructions
The Ketogenic Diet
Click to go to the Swiss Protocol Ketogenic Diet
Click to go to the Ketogenic Diet Resource
MAP® - Master Amino Acid Pattern
Take MAP® to support the Ketogenic Diet (protein without glucose) and to build muscle mass and the immune system (Used in the Swiss Protocol).
Click to go to the European manufacture's website Master Amino acid Pattern
Click to go to the South Pacific distributor´s website.The Swiss Protocol MAP®
In General
- Walk for 30 to 60 minutes each day
- Be emotionally positive (grateful and quick to forgive)
- Get a good nights sleep
- Keep hydrated
- Bathe in sunlight most days
New Zealand Immunotherapy Centre
Auckland: For Cancer, Chronic Fatigue, Neurodegenerative Diseases and Neurodevelopmental Diseases (Autism).
Note: New Zealand medical doctors cannot advertise they treat with GcMAF.
Japanese Immunotherapy Centres
Kobe: For Cancer.
Inui: For Cancer, Hepatitis and Chronic Diseases.
Keihan: For Cancer, Hepatitis and Chronic Diseases.
R Mirai (vezi nota de mai sus, ca nu au raportat rezultate incurajatoare): For Cancer.
Australian GcMAF Medical Support
Queensland: For Immunotherapy.
Paraguay
Hernandarias: For Immunotherapy and Stem Cell therapy.
Se poate cumpara GcMAF cu administrare orala:
Buy "oral" Bravo GcMAF Probiotic Yoghurt
Produces by natural fermentation approx 490ng of OA-GcMAF in every litre.
- Contains lactoferrins & immunoglobulins.
- Contains 42 microbial strains.
- Contains Organic Swiss Colostrum.
- Is rich in minerals, vitamins & bio-active molecules.
- Used in the immunotherapy clinics alongside injectable GcMAF.
- Strong enough to fully activate your immune system within 3 weeks of use.
At Immuno Biotech Ltd we wrote 16 research papers on GcMAF in 2013. All peer reviewed and published in prestigious scientific journals or immunology conferences.
Here is the list on the US Library of Medicine, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed searching on:
GcMAF OR “vitamin D binding protein” AND “macrophage activating factor”
1: Toyohara Y, Hashitani S, Kishimoto H, Noguchi K, Yamamoto N, Urade M. Inhibitory effect of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor on DMBA-induced hamster cheek pouch carcinogenesis and its derived carcinoma cell line. Oncol Lett. 2011 Jul;2(4):685-691. Epub 2011 May 13. PubMed PMID: 22848250; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3406437.
2: Bellone M, Rigamonti N. Vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor, GcMAF, and prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012 Dec;61(12):2377-8. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1310-9. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PubMed PMID: 22740161.
3: Uto Y, Yamamoto S, Mukai H, Ishiyama N, Takeuchi R, Nakagawa Y, Hirota K, Terada H, Onizuka S, Hori H. ?-Galactosidase treatment is a common first-stage modification of the three major subtypes of Gc protein to GcMAF. Anticancer Res. 2012 Jun;32(6):2359-64. PubMed PMID: 22641675.
4: Pacini S, Punzi T, Morucci G, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M. Effects of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor on human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012 Jan;32(1):45-52. PubMed PMID: 22213287.
5: Pacini S, Morucci G, Punzi T, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M, Amato M, Aterini S. Effect of paricalcitol and GcMAF on angiogenesis and human peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation and signaling. J Nephrol. 2012 Jul-Aug;25(4):577-81. doi: 10.5301/jn.5000035. PubMed PMID: 21956771.
6: Uto Y, Yamamoto S, Takeuchi R, Nakagawa Y, Hirota K, Terada H, Onizuka S, Nakata E, Hori H. Effect of the Gc-derived macrophage-activating factor precursor (preGcMAF) on phagocytic activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages. Anticancer
Res. 2011 Jul;31(7):2489-92. PubMed PMID: 21873164.
7: Debruyne E, Speeckaert M, Weygaerde YV, Delanghe J. Phenotype of Gc-globulin influences the macrophage activating factor (MAF) levels in serum. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011 Nov;49(11):1855-60. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.676. Epub 2011 Aug 23. PubMed PMID: 21859424.
8: Pacini S, Morucci G, Punzi T, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M. Gc protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) stimulates cAMP formation in human mononuclear cells and inhibits angiogenesis in chick embryo chorionallantoic
membrane assay. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Apr;60(4):479-85. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0953-7. Epub 2010 Dec 14. PubMed PMID: 21170647.
9: Faserl K, Golderer G, Kremser L, Lindner H, Sarg B, Wildt L, Seeber B. Polymorphism in vitamin D-binding protein as a genetic risk factor in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jan;96(1):E233-41. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1532. Epub 2010 Oct 27. PubMed PMID: 20980430.
10: Gregory KJ, Zhao B, Bielenberg DR, Dridi S, Wu J, Jiang W, Huang B, Pirie-Shepherd S, Fannon M. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor directly inhibits proliferation, migration, and uPAR expression of prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 2010 Oct 18;5(10):e13428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013428. PubMed PMID: 20976141; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2956649.
11: Nonaka K, Onizuka S, Ishibashi H, Uto Y, Hori H, Nakayama T, Matsuura N, Kanematsu T, Fujioka H. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor inhibits HCC in SCID mice. J Surg Res. 2012 Jan;172(1):116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.07.057. Epub 2010 Sep 17. PubMed PMID: 20855083.
12: Ravnsborg T, Olsen DT, Thysen AH, Christiansen M, Houen G, Højrup P. The glycosylation and characterization of the candidate Gc macrophage activating factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Apr;1804(4):909-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.12.022. Epub 2010 Jan 13. PubMed PMID: 20079467.
13: Rehder DS, Nelson RW, Borges CR. Glycosylation status of vitamin D binding protein in cancer patients. Protein Sci. 2009 Oct;18(10):2036-42. doi: 10.1002/pro.214. PubMed PMID: 19642159; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2786967.
14: Fang Y, van Meurs JB, Arp P, van Leeuwen JP, Hofman A, Pols HA, Uitterlinden AG. Vitamin D binding protein genotype and osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009 Aug;85(2):85-93. doi: 10.1007/s00223-009-9251-9. Epub 2009 Jun 2. PubMed PMID: 19488670; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2729412.
15: Yamamoto N, Ushijima N, Koga Y. Immunotherapy of HIV-infected patients with Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF). J Med Virol. 2009 Jan;81(1):16-26. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21376. PubMed PMID: 19031451.
16: Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Yamamoto N. Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer with Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor, GcMAF. Transl Oncol. 2008 Jul;1(2):65-72. PubMed PMID: 18633461; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2510818.
17: Spiriti J, Bogani F, van der Vaart A, Ghirlanda G. Modulation of protein stability by O-glycosylation in a designed Gc-MAF analog. Biophys Chem. 2008 May;134(3):157-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2008.02.005. Epub 2008 Feb 21. PubMed PMID:
18329161.
18: Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Nakazato H, Yamamoto N, Koga Y. Immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor, GcMAF. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008
Jul;57(7):1007-16. PubMed PMID: 18058096.
19: Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Yamamoto N, Ushijima N. Immunotherapy of metastatic breast cancer patients with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF). Int J Cancer. 2008 Jan 15;122(2):461-7. PubMed PMID:
17935130.
20: Meier U, Gressner O, Lammert F, Gressner AM. Gc-globulin: roles in response to injury. Clin Chem. 2006 Jul;52(7):1247-53. Epub 2006 May 18. Review. PubMed PMID: 16709624.
21: Kalkunte S, Brard L, Granai CO, Swamy N. Inhibition of angiogenesis by vitamin D-binding protein: characterization of anti-endothelial activity of DBP-maf. Angiogenesis. 2005;8(4):349-60. Epub 2006 Jan 7. PubMed PMID: 16400520.
22: Yamamoto N, Urade M. Pathogenic significance of alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity found in the hemagglutinin of influenza virus. Microbes Infect. 2005 Apr;7(4):674-81. Epub 2005 Mar 22. PubMed PMID: 15848273.
23: Nagasawa H, Sasaki H, Uto Y, Kubo S, Hori H. Association of the macrophage activating factor (MAF) precursor activity with polymorphism in vitamin D-binding protein. Anticancer Res. 2004 Sep-Oct;24(5C):3361-6. PubMed PMID: 15515432.
24: Onizuka S, Kawakami S, Taniguchi K, Fujioka H, Miyashita K. Pancreatic carcinogenesis: apoptosis and angiogenesis. Pancreas. 2004 Apr;28(3):317-9. PubMed PMID: 15084979.
25: Matsuura T, Uematsu T, Yamaoka M, Furusawa K. Effect of salivary gland adenocarcinoma cell-derived alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase on the bioactivity of macrophage activating factor. Int J Oncol. 2004 Mar;24(3):521-8. PubMed PMID: 14767536.
26: Schneider GB, Grecco KJ, Safadi FF, Popoff SN. The anabolic effects of vitamin D-binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-MAF) and a novel small peptide on bone. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2003;13(2-4):277-84. PubMed
PMID: 14696974.
27: Mohamad SB, Nagasawa H, Sasaki H, Uto Y, Nakagawa Y, Kawashima K, Hori H. Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF): isoelectric focusing pattern and tumoricidal activity. Anticancer Res. 2003 Nov-Dec;23(6a):4451-7. PubMed PMID: 14666733.
28: Gumireddy K, Reddy CD, Swamy N. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates DBP-maf-induced apoptosis in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Cell Biochem. 2003 Sep 1;90(1):87-96. PubMed PMID: 12938159.
29: Kisker O, Onizuka S, Becker CM, Fannon M, Flynn E, D’Amato R, Zetter B, Folkman J, Ray R, Swamy N, Pirie-Shepherd S. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-maf) inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in mice.
Neoplasia. 2003 Jan-Feb;5(1):32-40. PubMed PMID: 12659668; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1502120.
30: Mohamad SB, Nagasawa H, Uto Y, Hori H. Preparation of Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF) and its structural characterization and biological activities. Anticancer Res. 2002 Nov-Dec;22(6C):4297-300. PubMed PMID:
12553073.
31: Kanda S, Mochizuki Y, Miyata Y, Kanetake H, Yamamoto N. Effects of vitamin D(3)-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF) on angiogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002 Sep 4;94(17):1311-9. PubMed PMID: 12208896.
32: Swamy N, Ghosh S, Schneider GB, Ray R. Baculovirus-expressed vitamin D-binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-maf) activates osteoclasts and binding of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) does not influence this activity. J Cell Biochem. 2001;81(3):535-46. PubMed PMID: 11255236.
33: Kanan RM, Cook DB, Datta HK. Lectin immunoassay for macrophage-activating factor (Gc-MAF) produced by deglycosylation of Gc-globulin: evidence for noninducible generation of Gc-MAF. Clin Chem. 2000 Mar;46(3):412-4. PubMed PMID: 10702530.
34: Odgren PR, Popoff SN, Safadi FF, MacKay CA, Mason-Savas A, Seifert MF, Marks SC Jr. The toothless osteopetrotic rat has a normal vitamin D-binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-MAF) cascade and chondrodysplasia resistant to treatments with colony stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and/or DBP-MAF. Bone. 1999 Aug;25(2):175-81. PubMed PMID: 10456382.
35: Koga Y, Naraparaju VR, Yamamoto N. Antitumor effect of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor on Ehrlich ascites tumor-bearing mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1999 Jan;220(1):20-6. PubMed PMID: 9893164.
36: Adebanjo OA, Moonga BS, Haddad JG, Huang CL, Zaidi M. A possible new role for vitamin D-binding protein in osteoclast control: inhibition of extracellular Ca2+ sensing at low physiological concentrations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Aug 28;249(3):668-71. PubMed PMID: 9731194.
37: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR. Structurally well-defined macrophage activating factor derived from vitamin D3-binding protein has a potent adjuvant activity for immunization. Immunol Cell Biol. 1998 Jun;76(3):237-44. PubMed PMID: 9682967.
38: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR. Immunotherapy of BALB/c mice bearing Ehrlich ascites tumor with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor. Cancer Res. 1997 Jun 1;57(11):2187-92. PubMed PMID: 9187119.
39: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Moore M, Brent LH. Deglycosylation of serum vitamin D3-binding protein by alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase detected in the plasma of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol.
1997 Mar;82(3):290-8. PubMed PMID: 9073553.
40: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Urade M. Prognostic utility of serum alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase and immunosuppression resulted from deglycosylation of serum Gc protein in oral cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1997 Jan
15;57(2):295-9. PubMed PMID: 9000571.
41: Korbelik M, Naraparaju VR, Yamamoto N. Macrophage-directed immunotherapy as adjuvant to photodynamic therapy of cancer. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(2):202-7. PubMed PMID: 9010027; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2063270.
42: Benis KA, Schneider GB. The effects of vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor and colony-stimulating factor-1 on hematopoietic cells in normal and osteopetrotic rats. Blood. 1996 Oct 15;88(8):2898-905. PubMed PMID:
8874186.
43: Yamamoto N. Structural definition of a potent macrophage activating factor derived from vitamin D3-binding protein with adjuvant activity for antibody production. Mol Immunol. 1996 Oct;33(15):1157-64. PubMed PMID: 9070663.
44: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR. Role of vitamin D3-binding protein in activation of mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 15;157(4):1744-9. PubMed PMID: 8759764.
45: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Orchard PJ. Defective lymphocyte glycosidases in the macrophage activation cascade of juvenile osteopetrosis. Blood. 1996 Aug 15;88(4):1473-8. PubMed PMID: 8695868.
46: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR. A defect in inducible beta-galactosidase of B lymphocytes in the osteopetrotic (mi/mi) mouse. Immunology. 1996 Aug;88(4):604-10. PubMed PMID: 8881764; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1456628.
47: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Asbell SO. Deglycosylation of serum vitamin D3-binding protein leads to immunosuppression in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1996 Jun 15;56(12):2827-31. PubMed PMID: 8665521.
48: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR. Vitamin D3-binding protein as a precursor for macrophage activating factor in the inflammation-primed macrophage activation cascade in rats. Cell Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;170(2):161-7. PubMed PMID: 8660814.
49: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR. A defect in beta-galactosidase of B lymphocytes in the osteopetrotic (op/op) mouse. Immunol Lett. 1996 Apr;50(1-2):35-40. PubMed PMID: 8793557.
50: Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Srinivasula SM. Structural modification of serum vitamin D3-binding protein and immunosuppression in AIDS patients. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1995 Nov;11(11):1373-8. PubMed PMID: 8573395.
51: Schneider GB, Benis KA, Flay NW, Ireland RA, Popoff SN. Effects of vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-MAF) infusion on bone resorption in two osteopetrotic mutations. Bone. 1995 Jun;16(6):657-62. PubMed
PMID: 7669443.
52: Naraparaju VR, Yamamoto N. Roles of beta-galactosidase of B lymphocytes and sialidase of T lymphocytes in inflammation-primed activation of macrophages. Immunol Lett. 1994 Dec;43(3):143-8. PubMed PMID: 7721326.
53: Yamamoto N, Willett NP, Lindsay DD. Participation of serum proteins in the inflammation-primed activation of macrophages. Inflammation. 1994 Jun;18(3):311-22. PubMed PMID: 8088927.
54: Yamamoto N, Lindsay DD, Naraparaju VR, Ireland RA, Popoff SN. A defect in the inflammation-primed macrophage-activation cascade in osteopetrotic rats. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):5100-7. PubMed PMID: 8176226.
55: Yamamoto N, Kumashiro R. Conversion of vitamin D3 binding protein (group-specific component) to a macrophage activating factor by the stepwise action of beta-galactosidase of B cells and sialidase of T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2794-802. PubMed PMID: 8360493.
56: Homma S, Yamamoto M, Yamamoto N. Vitamin D-binding protein (group-specific component) is the sole serum protein required for macrophage activation after treatment of peritoneal cells with lysophosphatidylcholine. Immunol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;71 ( Pt 4):249-57. PubMed PMID: 8225394.
57: Yamamoto N, Homma S, Haddad JG, Kowalski MA. Vitamin D3 binding protein required for in vitro activation of macrophages after alkylglycerol treatment of mouse peritoneal cells. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):420-4. PubMed PMID: 1769691; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1384634.
58: Yamamoto N, Homma S. Vitamin D3 binding protein (group-specific component) is a precursor for the macrophage-activating signal factor from lysophosphatidylcholine-treated lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8539-43. PubMed PMID: 1924312; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC52544.
59: Yamamoto N, Homma S, Millman I. Identification of the serum factor required for in vitro activation of macrophages. Role of vitamin D3-binding protein (group specific component, Gc) in lysophospholipid activation of mouse peritoneal
macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):273-80. PubMed PMID: 2051023.
Prezentari video sustinute de David Noakes:
https://www.change.org/p/house-of-commons-to-disband-the-medicines-and-healthcare-products-regulatory-agency-mhra-a-corrupt-government-body-charged-with-protecting-patients-from-avoidable-harm-in-the-national-health-service-and-in-public-health
Nagalase Testing
High Nagalase indicates that your condition may be successfully treated with GcMAF.Testing in the USAHealth Diagnostics and Research Institute. New Jersey
Testing in EuropeEuropean Laboratory of Nutrients. Netherlands
R.E.D. Laboratories. Belgium
Testing in the South PacificSt Benedicts Health Care
A normal healthy Nagalase result is under 0.62, whereas a reading of 7 is very high.
In general, a cancer patient severity rating based on the Nagalase result is ...
- 0.62 to 2 minor
- 2 to 3 moderate
- 3 to 5 major
- 5 to 7 severe
Monocyte Count
A patients monocyte count will generally rise in the early stages of GcMAF treatment and indicates a response to GcMAF.Note: Monocytes in the blood vessels become Macrophages in the tissues.
Prognostic Inflammatory and Nutritional Index (PINI) (2)
Calculated by dividing the product of serum alpha-1-glycoprotein and CRP levels by that of albumin and pre-albumin.
alpha-1-glycoprotein (mg/dl) x CRP (mg/dl)
albumin (g/dl) x prealbumin (mg/dl)
albumin (g/dl) x prealbumin (mg/dl)
| > 30 | = | Predicts a very high risk of complications |
| [21-30] | = | Predicts a high risk of complications |
| [11-20] | = | Predicts an intermediate risk |
| [1-10] | = | Predicts a low risk |
| < 1 | = | Normal |
Your doctor can organise the blood tests required for the PINI score.
Genotyping - Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) polymorphisms
Testing in Europe R.E.D. Laboratories. BelgiumVirusii sau parazitii sunt un indiciu al organismului cu sistem imunitar slabit, intoxicat si predispus la cancer.
Virusii si parazitii nu patrund intr-un organism cu sistem imunitar sanatos. Daca sunt prezenti in organism, ei isi fac datoria de a dizolva si elimina acumularile toxice. Sunt pompierii prezenti la locul incendiului. Daca incendiul scapa de sub control, atunci se multiplica peste limita critica si sunt dispusi sa piara impreuna cu intregul organism. Decat sa starpim pompierii, mai bine ajutam la stingerea incendiului prin stimularea si intarirea naturala a sistemului imunitar, nu prin vaccinuri nocive.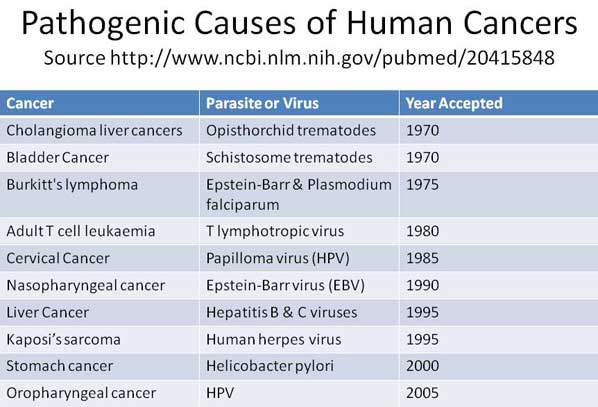
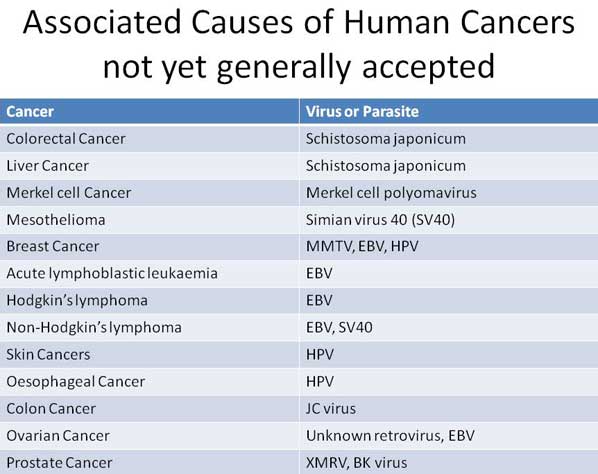
For more information on GcMAF, go to Biochemist's who make GcMAF. Veti obtine si preturi:
Clinicile Saisei Mirai http://www.saisei-mirai.jp/
Prin uciderea medicilor naturopati si disparitia altor 5 in SUA, care sunt in legatura cu subiectul GcMAF, tocmai au facut o reclama nedorita de concernele farmaceutice unui remediu pentru vindecarea cancerului si eliminarea vaccinurilor.
Exista sperante.
Pana se pune la punct un remediu sigur optati pentru suplimente naturale cu vitaminele B17, C, D (D3) si E.
Doamne ajuta!


